SCHEME OF WORK FOR THIRD TERM
WEEK
|
TOPIC
|
1
|
· REVIEW OF 2ND TERM EXAM QUESTION
· WRITING THE SCHEME OF WORK
|
2-4
|
PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT
·
Definition of program
·
Characteristics of a good
program
·
Steps in program development
·
Description of the steps in
program development
·
Compilation and
interpretation of program
·
How compiler and interpreter
works
|
5-6
|
ALGORITHM AND FLOWCHART
·
Definitions of algorithm and
flowchart
·
Functions of algorithm
·
Characteristics of algorithm
·
Writing algorithm for problem
solving
·
Flowchart symbols and their
uses
·
Flowchart examples
|
7-8
|
INTERNET
·
Definition of internet
·
Definition of terms – browse,
browser, chat room, cyber café, download, home page, e-mail, html, http,
internet service provider etc.
·
Internet services – e-mail,
search engine, telnet, ftp, www etc
·
Benefits of the internet
·
Problems of the internet
|
TOPIC ONE: PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT
Meaning of a Program
A computer program is
a general term used to describe the set of instructions that the computer use
to performs a specific task. A computer
program is usually written by a computer programmer using a programming
language.
Characteristics of a Good Program
A
good computer program should have following characteristics:
- Portability:
Portability refers to the ability of an application to run on different
platforms (operating systems) with or without minimal changes.
- Readability:
The program should be written in such a way that it makes other
programmers or users to follow the logic of the program without much
effort.
- Efficiency:
Every program requires certain processing time and memory to process the
instructions and data. A program should be laid out in such a manner that
it utilizes the least amount of memory and processing time.
- Structural:
To develop a program, the task must be broken down into a number of
subtasks which are developed independently, and each subtask is able to
perform the assigned job without the help of any other subtask. If a
program is developed structurally, it becomes more readable, and the
testing and documentation process also gets easier.
- Flexibility:
A good program should allow changes without having to rewrite the entire
program. Most programs are developed for a certain period and they require
modifications from time to time.
- Accuracy/Correctness:
Accuracy ensures that the program does what it is meant to do according to
the design specification.
- Generality:
Generality means that if a program is developed for a particular task,
then it should also be used for all similar tasks of the same domain. For
example, if a program is developed for a particular organization, then it
should suit all the other similar organizations.
- Maintainability:
Maintainability is the ease with which changes can be made to the program to satisfy
new requirements. Maintainability allows the program to be upgraded or revised
when the need arises.
- Reusability:
Reusability is the ease with which a program can be reused in developing other program.
By reusing existing program, developers can create more complex program in a
shorter amount of time.
- Clarity: The program should be clear enough to
be understood by others.
- Security: This ensures that the software
protects the information it is responsible for.
- User-friendliness: It ensures that the program is easy
to use by the intended users. It should have a sensitive user interface that
will enable the user to interact with the program without any difficulty.
- Robustness: The program should be provided with
the mechanism to respond to unexpected conditions, e.g., if wrong input is
entered into it.
Steps In Program Development
Before coding of a good program, there
must be a proper planning and steps on how the problem or program will be
stored.
The steps include the following:
- 1. Problem
definition
- 2. Problem
analysis
- 3. Algorithm/Flowcharting
- 4. Desk
checking
- 5. Program
coding
- 6. Program
compilation
- 7. Program
testing and debugging
- 8.
Program documentation.
- Problem
Definition: Entails defining and understanding
the problem statement and deciding the boundaries of the problem. In this phase
we need to understand the problem statement, what is our requirement, what
should be the output of the problem solution? These are defined in this first
phase of the program development life cycle.
- Problem Analysis:
The requirements like variables, functions, or resources to solve the problem are
gathered.
- Algorithm/Flowcharting:
During this phase, a step by step procedure to solve the problem using the
specification given in the previous phase is developed.
- Desk checking:
This involves manual checking of the logic of a program for correctness
- Coding: This phase involves
using a programming language to write or implement actual programming
instructions for the steps defined in the previous phase. In this phase, we
construct actual program. That means we write the program to solve the given
problem using programming languages like C, C++, Java etc.,
- Program compilation:
Compilation is the process whereby the source program (program written in other
language different from machine language), is translated into machine readable
code. A compiler does the job of compilation.
- Testing & Debugging:
During this phase, we check whether the code written in previous step is solving
the specified problem or not, i.e. check whether input data will provide
desired output or not.
- Maintenance:
During this phase, the program is actively used by the users. If the user
encounters any problem or wants any enhancement, then we need to repeat all the
phases from the starting, so that the encountered problem is solved or
enhancement is added.
- Documentation:
Program documentation includes hard-copy or electronic manuals that enable
users, program developers, and operators to interact successfully with a
program, e.g. user manual (a description of software commands and
troubleshooting guide).
Compilation
and interpretation of program
A compiler translates the entire
program (source code/program) written in a high level language into an
intermediate form called (object code/program), which can be directly executed
by the machine. On the other hand, an
interpreter does not produce an object code but translate the source program
line by line directly into machine language.
Examples
of compiled programs languages are: C, C++, C#, Ada, ALGOL, Java, COBOL,
Visual Basic, Lisp, FORTRAN, Pascal
Examples
of interpreted languages are: QBASIC, JavaScript, PHP, ASP, APL
How
a compiler works
The brain of the compiler is the
parser. It knows the syntax (rule) of the source language or the grammatical
rules that determine how the source statements are written. Whenever the parser
needs more of the source program statements to work on, it calls upon the
scanner. The scanner reads in the source program statement and breaks it into a
sequence of tokens – words, numbers, identifiers, operators etc. It hands them
one at a time to the parser whenever the parser calls for the next one.
The parser also
knows the semantics (meaning) of the source language. The parser’s knowledge of
the semantics enables it to call the code generator to produce the object code,
which performs the operation specified by the instruction. This continues until
the entire program has been read in and translated.
How
an interpreter works
Just like the
compiler, an interpreter also has a parser that controls it. Its scanner does
the same job as that of the compiler. However, an interpreter has an executor
instead of the code generator.
TOPIC TWO: ALGORITHM
AND FLOWCHART
Algorithm can also be defined as a procedure
consisting of a series of steps which specify a sequence of operations that
provides the solution to a problem.
An
algorithm is a finite set of an instruction that specifies a sequence of
operations to be carried out in order to solve a specific problem. It is a detailed sequence of simple
steps that are needed to solve a problem.
Pseudocode is a detailed yet readable description of an
algorithm, expressed in a formally-styled natural language rather than in a
programming language. It is very similar to everyday English.
A flowchart is a pictorial
representation of an algorithm in which the steps are drawn in the form of
different shapes of boxes and the logical flow is indicated by interconnecting
arrows.The boxes represent operations and the arrows represent the sequence in
which the operations are implemented.
A flowchart
is a diagrammatical representation of an algorithm.
Functions of
algorithm
- It
provides a step-by-step solution to a problem
- It
is used to prove that a problem has a solution
- It
is used to give a sense of direction to the steps of solving a problem
- It
may also be used to show that a problem does not have a solution
Characteristics
of an algorithm
- Finiteness:
it specifies an exact number of steps to be taken and has an end
- Absence of ambiguity:
it shows that every instruction is clearly and precisely specified
- Sequence of execution:
it shows how the instructions are performed from top to bottom
- Effectiveness:
it ensures that the solution prescribed is guaranteed to give a correct answer
and that the specified process is faithfully carried out.
- Input and output:
these defines the unknowns of the problem specified and the expected output
- Scope definition:
it specifies precisely the problem or class of problem
- Independence:
algorithm is language independent
ALGORITHM
Examples
Example 1: Calculate the Interest of a
Bank Deposit
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Read
amount,
Step 3: Read
years,
Step 4: Read
rate,
Step 5: Calculate
the interest with formula “Interest=Amount*Years*Rate/100
Step 6: Print interest
Step 7: Stop
Example 2: Algorithm to Determine and
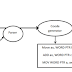
Output Whether Number N is Even or Odd
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Read number N,
Step 3: Set
remainder as N modulo (divide) 2,
Step 4: If
remainder is equal to 0 then number N is even, else number N is odd,
Step 5: Print
output.
Step 6: Stop
Example 3: Algorithm to Print 1 to 20:
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Initialize
X as 0,
Step 3: Increment
X by 1,
Step 4: Print X,
Step 5: If X is
less than 20 then go back to step 2.
Step 6: Stop
Flowchart symbols, name and uses
Below are the corresponding flowcharts
Flowchart for example 1: Calculate the Interest of a Bank Deposit
Flowchart for example 2: Determine and Output Whether Number N is
Even or Odd
Flowchart for example3: Print 1 to 20
TOPIC THREE: INTERNET
The Internet is the global system of
interconnected computer networks that use the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP)
to link billions of devices worldwide. It is an international network for communication,
where millions of computers are connected together. It is the largest computer
network in the world.
Definition of
some basic terms
- Home
page:
is an introductory page of a website, typically serving as a table of contents
for the site. It is an initial page or point of entry to all information stored
within.
- Web page: is a single
page of information on a website.
- Website: is a collection
of related web pages (document that are accessed through the internet),
typically identified with a common web address or domain name or URL (Uniform Resource Locator), published on
at least one web server. Examples are https://google.com, https://isi.ui.edu.ng,
https://facebook.com etc.
- HyperText Markup
Language, commonly
referred to as HTML, is the standard markup language used to create web
pages. Web browsers can read HTML files and render them into visible and
audible web pages.
- A protocol
can be defined as set of rules and regulations that determine how data is
transmitted in telecommunications and computer networking
- HyperText Transfer
Protocol, HTTP is the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web. HTTP defines how messages are
formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various
commands.
- Upload: this is the
process of transferring files from a local computer to another (remote)
computer on the World Wide Web.
- Cyber cafe: this is a place
to use computer to access the internet, create document, chat with friends
using voice and video as well as a number of other computer related tasks.
- Browser: A browser or a
web browser is an application program with a graphical user interface for
displaying HTML files, used to navigate the World Wide Web. Technically, a Web
browser is a client program that
uses HTTP (Hypertext
Transfer Protocol) to make requests of Web servers throughout the Internet on behalf of the
browser user. Examples include Mozilla Firefox,
Apple safari, Opera Mini, Lynx , Flock, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Netscape
Navigator, UC browser, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge etc.
- Internet Service
Provider (ISP):
an organization that provides individuals and other companies’ access to the
internet. Examples include MTN, Airtel, 9mobile, Smile etc.
Internet services
- · E-mail
(Electronic mail): this is a message sent from one person to
another, or many others through the internet connected computers.
- ·
Telnet is a user
command and an underlying TCP/IP protocol for accessing remote computers.
- · Usenet (Users network)
is an early non-centralized computer network for the discussion of particular
topics and the sharing of files via newsgroups. Newsgroups are Internet discussion forums where groups of
users with common interests gather to talk about everything from software to
comic books to politics.
- ·
File Transfer
Protocol (FTP)
is a standard network protocol used to transfer computer
files from one host
to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet.
- · World Wide Web
(WWW)
is a network of online content that is formatted in HTML (connected by
hyperlinks and URL) and accessed via HTTP. A system of Internet servers that
support specially formatted documents. The documents are formatted in a markup
language called HTML.
- ·
Search engine: this is a computer program that retrieves
documents or data from a database or from a computer network (especially from
the internet). It is an utility for finding information on the internet.
Benefits of the
internet
- ·
It provides quick access to almost any kind of
information
- · It is a fast, cheap and effective means of
communicating and exchanging information all over the world
- ·
E-commerce: buying and selling has been made
possible through the internet
- · Job opportunities such as graphic designing,
blogging, freelance writing etc. have been made possible
- ·
It is an avenue for advertisement of goods and
services
- ·
Online training and seminar called WEBINARS are
made possible
- · Online degree/E-learning: the internet
provides us the opportunity to learn and earn degree/certificates by taking
online classes.
- ·
Online banking
Abuse of the
internet
- ·
Hacking: using the internet to gain
unauthorized access to people’s computers
- ·
Fraud: fraudulent activity involves any
attempt to unlawfully obtain money from unsuspecting users
- · Copyright violation: someone’s electronic
content can be copied without due reference or permission
- · Virus distribution: internet users are prone
to downloading virus and other malicious program when downloading
software/files from illegitimate website on the internet.
- ·
Pornography: the internet is flooded with
websites that are pornographic in nature
- ·
Cyber bullying: using the internet to threaten
and bully someone
- ·
Spamming: sending unsolicited messages to
individual or network groups through the internet.